 PHP-RBAC
PHP-RBAC
PHP-RBAC is the de-facto authorization library for PHP. It provides developers with NIST Level 2 Standard Role Based Access Control and more, in the fastest implementation yet.
Why RBAC?
Role Based Access Control is the standard means of authorization (access control). The other approach is ACLs, where a table defines who can do what. ACLs are only good for very small systems, because of the following reasons:
 Big systems have lots of permits
Big systems have lots of permits People move in organizations, and all their permits should be changed when they do
People move in organizations, and all their permits should be changed when they do Maintenance (adding, changing, removing) of 100,000 permits requires a handful of staff
Maintenance (adding, changing, removing) of 100,000 permits requires a handful of staff Maintenance of the permits assigned to each user, requires more staff than above!
Maintenance of the permits assigned to each user, requires more staff than above! One wrong user-permit and you have a serious breach in your security, so no room for error
One wrong user-permit and you have a serious breach in your security, so no room for error
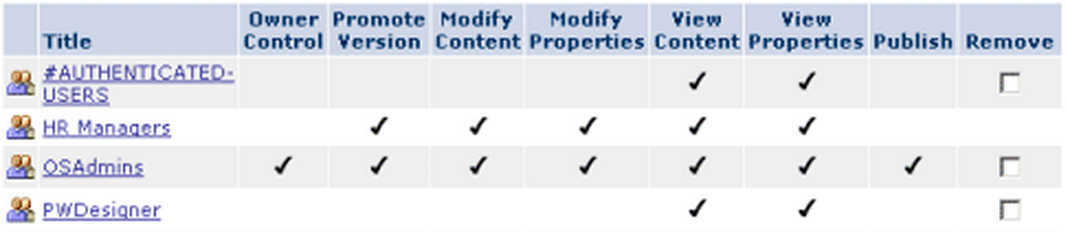
Example of an ACL
Usage of ACLs has led to broken authorization and access control all over applications, and authorization is limited only to critical operations to keep number of permits low.
But RBAC is here to save the day.
What is RBAC?
RBAC separates the concepts of Users, Roles and Permissions. Roles are defined in a system, then Permissions defined separately. Then the security administrator decides what role should be permitted to do what action, by assigning that role to the permission. Finally users are assigned to roles. The system does the rest.
 Still lots of permits in the system are the problem
Still lots of permits in the system are the problem People move, and only their roles need to be changed
People move, and only their roles need to be changed Maintenance of permits is still an issue
Maintenance of permits is still an issue Maintenance of permits assigned to each role is easy, it doesn't change much logically.
Maintenance of permits assigned to each role is easy, it doesn't change much logically. Role-Permission assignments can be double checked so that no wrong permit is given to any role
Role-Permission assignments can be double checked so that no wrong permit is given to any role
That was NIST Level 1 standard RBAC above, and it still had issues. NIST Level 2 RBAC requires Roles and/or Permissions to be hierarchical, so that management of them can easily be handled in hierarchies. The figure below demonstrates a system in hierarchical RBAC:
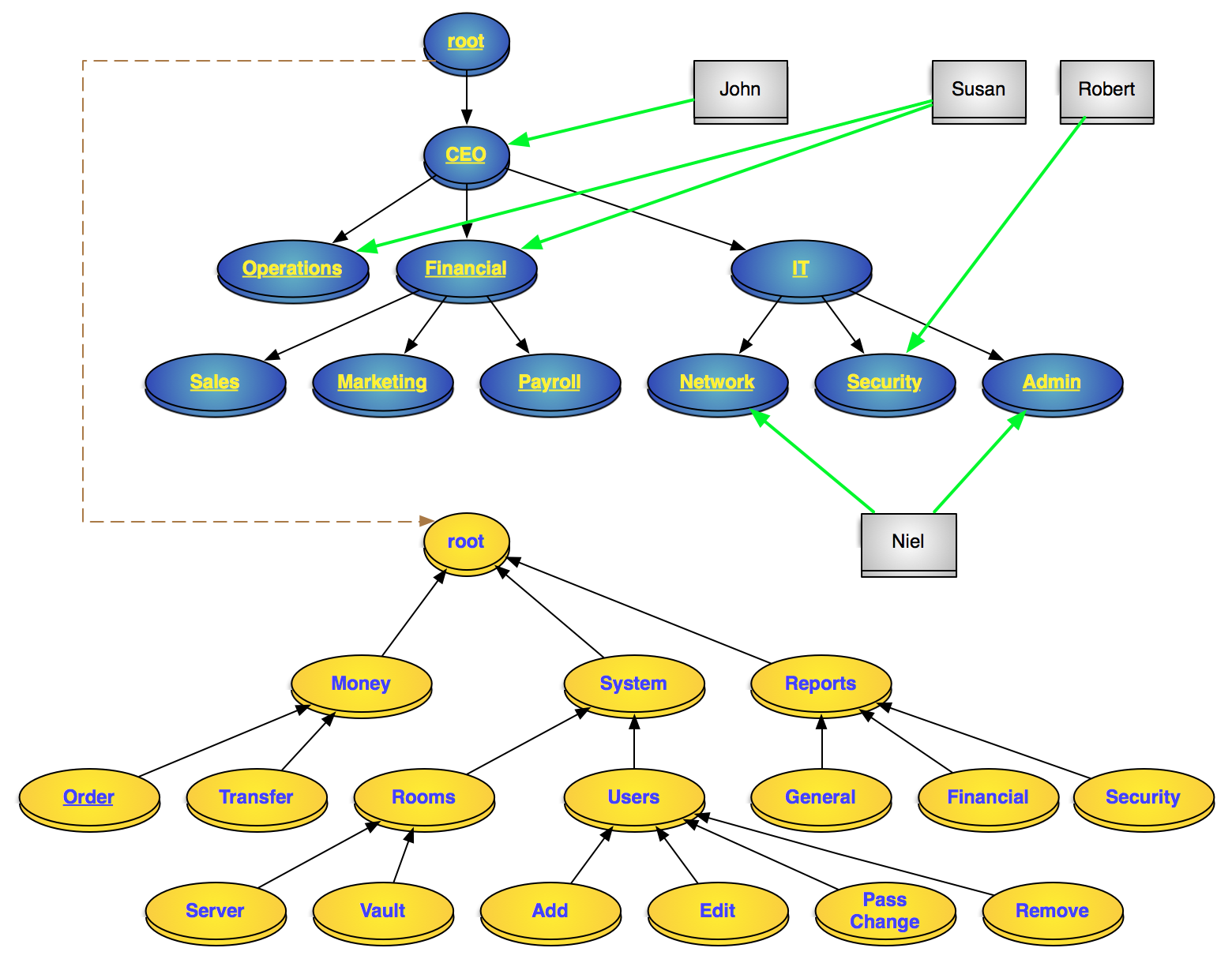
A hierarchical RBAC model of a system
Blue: roles, Gray: users, Yellow: permissions
Continue...
You are now ready for the next step: Before you begin